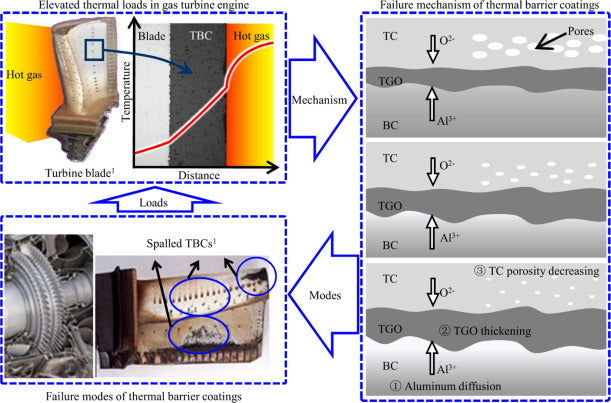
Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) play a crucial role in insulating components that operate at high temperatures, such as those found in gas turbines and aeroengines. Common applications include turbine blades, combustor cans, ducting, and nozzle guide vanes. TBCs have enabled higher operating temperatures in gas turbines, enhancing their performance and efficiency.
One of the defining features of TBCs is their exceptionally low thermal conductivity, which allows them to maintain a significant temperature gradient under heat exposure. The most widely used TBC material is yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ). YSZ is known for its resistance to thermal shock and thermal fatigue at temperatures up to 1150°C. It is typically applied using plasma spraying or electron beam physical vapor deposition (EBPVD). In some cases, high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spraying is used, particularly for applications like blade tip wear prevention, where the wear-resistant properties of YSZ are advantageous.
To ensure the durability and effectiveness of the TBC system, the substrate—usually a nickel or cobalt-based superalloy—is often aluminized and pre-coated with an MCrAlY bond coat. This bond coat is essential for managing residual stresses that may arise due to differences in the thermal expansion coefficients of the metallic substrate and the ceramic TBC.
Types of Coatings
- Anodic Coatings
- Cathodic Coatings
- Neutral Coatings
Benefits of Thermal Barrier Coatings
Thermal spray coatings are extensively used to prevent corrosion and offer additional benefits such as enhanced wear resistance. Key advantages include:
- Increased engine power
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Improved thermal conductivity
- Extended lifespan of components
- Protection from extreme temperatures
Application Technology
Portech provides advanced atmospheric plasma spray systems equipped with mass flow controllers. These systems operate under optimal parameters, delivering high-quality thermal barrier coatings tailored to specific requirements.